Introduction
In the era of rapid technological advancement, the demand for specialized imaging solutions has surged across various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and security systems. Custom camera modules have become a pivotal component in this landscape, enabling tailored imaging solutions that meet specific requirements. This article delves into the intricacies of custom camera module design, exploring its key elements, processes, and applications.
Understanding Camera Modules
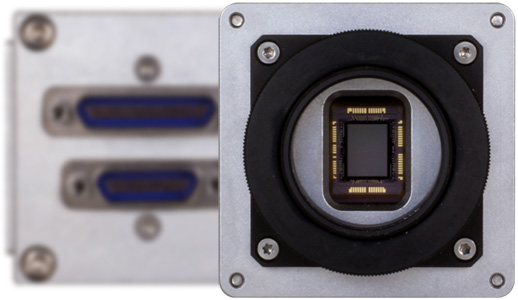
A camera module is a compact assembly that includes an image sensor, lens, and various electronic components that work together to capture images. While off-the-shelf camera modules are readily available, custom designs allow for greater flexibility and optimization for specific use cases.
Key Components of a Camera Module
- Image Sensor: The heart of the camera, responsible for converting light into electrical signals. Common types include CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors, each offering unique advantages in terms of image quality, power consumption, and speed.
- Lens: The optical component that focuses light onto the image sensor. Lens selection is crucial, as factors like focal length, aperture size, and field of view directly impact image quality and performance.
- Circuit Board: Houses the electronic components necessary for signal processing, control, and communication with other devices. Custom circuit designs can enhance performance and enable specific functionalities.
- Housing and Mounting: Protects the internal components and provides a means for integration into other systems. Custom housings can be designed to meet specific environmental or aesthetic requirements.
The Design Process
Designing a custom camera module involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and operational specifications.
1. Requirements Gathering
The first step is to define the specific requirements based on the intended application. This includes resolution, frame rate, size, weight, power consumption, and environmental conditions. Collaboration with stakeholders is vital to ensure all needs are addressed.
2. Component Selection
Once requirements are established, the next step is selecting appropriate components. This may involve:
- Choosing the Right Image Sensor: Consideration of factors like sensitivity, dynamic range, and noise performance.
- Lens Specifications: Determining the ideal focal length and aperture size based on the desired field of view and depth of field.
3. Prototyping
Creating a prototype is essential for testing and validation. This stage allows designers to evaluate the performance of the module under real-world conditions and make necessary adjustments. Rapid prototyping techniques, such as 3D printing and circuit simulation, can expedite this phase.
4. Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing is conducted to assess image quality, durability, and functionality. This can include:
- Image Quality Tests: Evaluating sharpness, color accuracy, and low-light performance.
- Environmental Testing: Ensuring the module can withstand temperature extremes, humidity, and mechanical stress.
5. Finalization and Production
After successful testing, the design is finalized, and preparations for mass production commence. This phase includes designing for manufacturability on optivistech, ensuring quality control processes are in place, and addressing any regulatory compliance requirements.
Applications of Custom Camera Modules
Custom camera modules have found applications in various sectors:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones and smart home devices often require unique imaging capabilities, prompting custom designs for enhanced features like low-light performance or wide-angle views.
- Automotive: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) rely on custom camera modules for functions such as lane departure warnings, parking assistance, and collision avoidance.
- Medical Devices: In applications like endoscopy or telemedicine, custom cameras can provide the necessary precision and imaging quality for diagnostics.
- Security Systems: Tailored camera solutions are essential for surveillance applications, where specific features like infrared imaging or high-resolution capabilities are critical.